GPS, GIS and their uses
GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM (GPS)
 Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite based navigation system that can provide people who use it with their exact position on Earth, tell them how to get to another location, how fast they are moving, where they have been, how far they have gone, what time it is, and many more.
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite based navigation system that can provide people who use it with their exact position on Earth, tell them how to get to another location, how fast they are moving, where they have been, how far they have gone, what time it is, and many more.
GPS was originally designed to help the U.S. military with finding the accurate location of their soldiers, vehicles, planes and ships around the world. Now, GPS is used in cellular phones, outdoor recreation, emergency services, navigation and map making. It is also used a lot in scientific research. For example, meteorologists use GPS to forecast the weather and geologists use it to measure earthquake movement.
SEGMENTS OF GPS:
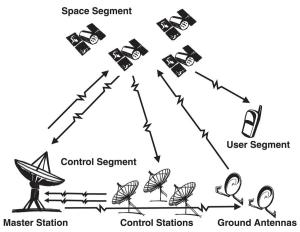
GPS consists of three segments i.e. Space, Control, and User.
-
Space Segment consists of 29 satellites circling the earth every 12 hours at 12,000 miles in altitude.
-
control segment tracks the satellites and then provides them with corrected orbital and time information.
-
User segment consists of the users and their GPS receivers. The number of simultaneous users is limitless.
HOW GPS DETERMINES A POSITION:
- When a GPS receiver is first turned on, it downloads orbit information from all the satellites called an almanac. This process, the first time, can take as long as 12 minutes; but once this information is downloaded, it is stored in the receiver’s memory for future use.
- The GPS receiver calculates the distance from each satellite to the receiver by using the distance formula: distance = velocity x time.
- The receiver determines position by using triangulation. When it receives signals from at least three satellites the receiver should be able to calculate its approximate position (a 2D position). The receiver needs at least four or more satellites to calculate a more accurate 3D position. The position can be reported in latitude/longitude, UTM, or other coordinate system.
GIS (GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM):
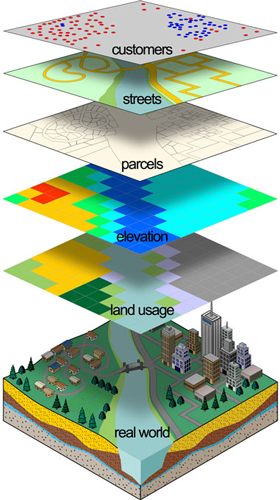 Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates common database operations such as query and statistical analysis with the unique visualization and geographic analysis benefits offered by maps. These abilities distinguish GIS from other information systems and make it valuable to a wide range of public and private enterprises for explaining events, predicting outcomes, and planning strategies.
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer based tool for mapping and analyzing spatial data. GIS technology integrates common database operations such as query and statistical analysis with the unique visualization and geographic analysis benefits offered by maps. These abilities distinguish GIS from other information systems and make it valuable to a wide range of public and private enterprises for explaining events, predicting outcomes, and planning strategies.
Many have characterized GIS as one of the most powerful of all information technologies because it focuses on integrating knowledge from multiple sources (for example, as layers within a map) and creates a crosscutting environment for collaboration.
Map making and geographic analysis are not new, but a GIS performs these tasks better and faster than do the old manual methods.GIS can be regarded as the high‐tech equivalent of the map.
COMPONENTS OF A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM
The components of GIS are:
- Hardware: Hardware includes the computer on which a GIS operates, the monitor on which results are displayed, and a printer for making hard copies of the results.
- Software: GIS software provides the functions and tools needed to store, analyze, and display geographic information.
- Data: It is the most important component of GIS. A GIS will integrate spatial data with other data resources and can even use a database management system used by most organizations to organize and maintain their data, to manage spatial data.
- People: GIS users range from technical specialists who design and maintain the system to those who use it to help them
 perform their everyday work.
perform their everyday work. - Methods: A successful GIS operates according to a well-designed plan and business rules, which are the models and operating practices unique to each organization.
A GIS works by storing the information about the world as a collection of thematic layers that can be linked together by geography. This simple but extremely powerful and versatile concept has proven invaluable for solving many real-world problems from modeling global atmospheric circulation, to predicting rural land use, and monitoring changes in rainforest ecosystems.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GPS AND GIS:
GPS is a satellite system that projects information to GPS receivers on the ground, enabling users to determine latitude and longitude coordinates whereas GIS is a Software program that enable users to store and manipulate large amounts of data from GPS and other sources.
Lets deal with example: GPS: An agricultural producer may use a handheld GPS receiver to determine the latitude and longitude coordinates of a water source next to a field or vineyard. GIS: Following a chemical spill, maps obtained from a GIS system can reveal environmentally sensitive areas that should be protected during response and recovery phases.
USE OF GPS IN AGRICULTURE:
The use of GPS technology in agriculture and farming is increasing rapidly. Some of the uses are listed below that it has been used or might be used in the future.
- Soil Sampling: Collecting soil samples across a large property can be organized using GPS and mapping software. The sample locations can be way pointed in the field and those waypoints marked on the mapping software. Then, when the laboratory results are returned the data can be plotted on the maps and decisions for soil treatment can be made for various parts of the property. The locational information can save money and time by allowing variable rate applications and treating only those areas with a documented need.
- Tractor Guidance: Farmers cannot put their tractors on auto-pilot. If they plow their fields with a recording GPS system the tractor can then be programmed to follow the same route for cultivating, fertilizing, pest control and harvesting.
- Crop-duster Targeting: Insects don’t attack a field with a uniform distribution. Workers strolling the crops can use a GPS to record the locations of insect problems. The data can then be used by cropduster pilots to selectively target the problem areas instead of treating an entire field. This method results in a savings of time, fuel, insecticide and crop exposure to chemicals.
- Tracking Livestock: The location of valuable animals on a large farm can be monitored by GPS transmitters attached to the animals collar. When the animals are sent to market GPS transmitters can also be used to track their location.
- Yield Monitoring: Estimates of yield variations across a property can be made using GPS. To do this the property is divided into zones and the yield of each zone is estimated and plotted on a map. The map can then be used to better understand the property and for decision-making in regard to the next planting.


I cherished up to you’ll obtain performed proper here. The comic strip is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an shakiness over that you want be turning in the following. sick indisputably come further in the past again as precisely the similar nearly very regularly inside case you protect this hike.
4r9hVQ Thank you ever so for you blog.Really thank you!
You are welcome guys!
n thanks 4 ur comments.
HSSWK0 Say, you got a nice blog.Much thanks again. Want more.
U r welcome!
I’ll do my best.
cfcLdm I truly appreciate this blog post.Thanks Again.
u r most welcome!
CwBjx4 Thank you for your article post.Really thank you! Really Cool.
a6WQ9c Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic article. Really Great.
You are welcome!!!
thankyou , this really helped , i have a geography end of year test so this really helped get my grades up , thanks .